CBSE Class VIII (8th) Science
Chapter 6. COMBUSTION AND FLAME
Lesson Exercises
Question 1. List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer : Conditions under which combustion take places :
- Some Fuel is is required for combustion. During combustion a fuel substance reacts with oxygen to give off heat.The fuel may be solid, liquid or gas.
- Oxygen in air is essential for combustion. Combustion can not take place in the absence of air (oxygen).
- For a combustion, an inflamabe substance must be heated to its ignition tempreture. Ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a combustible substance catches fire.
Question 2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Burning of wood and coal causes Pollution of air.
(b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is kerosene .
(c) Fuel must be heated to its Ignition temperature before it starts burning.
(d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by water .
Question 3. Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer : Our cities generally have high numbers of automobiles vehicals. The use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles is a major cause of air pollution to day. During combustion, these fuel release unburnt carbon particles. These fine particles are dangerous pollutants causing respiratory diseases, such as asthma.Incomplete combustion of these fuels gives carbon monoxide gas. It is a very poisonous gas.Combustion of most fuels releases carbon dioxide in the environment. Increased emission of carbon dioxide in the air is one of the major cause for global warming.
The use of diesel and petrol as fuels in automobiles is being replaced by CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), because CNG produces the harmful products in very small amounts. CNG is a cleaner fuel. It has high fuel efficiency. Hence use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities to a noticable extent .
Question 4. Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer :
| Comparasion LPG and Wood as Fuel | |
| LPG | Wood as Fuel |
|
|
Question 5. Give reasons:
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not.
Answer :
(a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment : As water may conduct electricity and harm those trying to douse the fire.
(b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood : As LPG is a affordable, readily available, combustible and easy to transport in cyllinders and tanker.
LPG is more energy efficient. Its calorific value is 55000 kJ/kg where as that of wood is just 17000-22000 kJ/kg. It causes less air pollution and prevent deforestation by supplimenting the fuel need in place of wood as fuel
(c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not : Because for burning or combustion, a substance must me heated to its ignition temperature. Paper wrapped around an aluminium pipe does not catch fire as on heating, it is unable to attain the ignition temperature due to transfer of heat to aluminium pipe which is good conductor of heat.
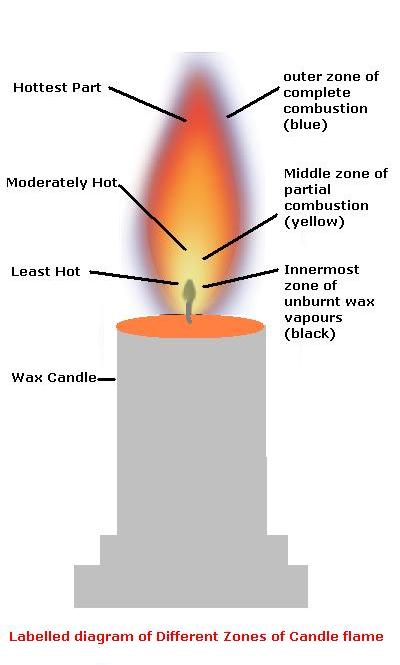
Question 6. Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer :
Question 7. Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer : The amount of heat energy produced on complete combustion of 1 kg of a fuel is called its calorific value. The calorific value of a fuel is expressed in a unit called kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Question 8. Explain how CO2 is able to control fires.
Answer : CO2, being heavier than oxygen, covers the fire like a blanket. Since the contact between the fuel and oxygen is cut off, the fire is controlled. For fires involving electrical equipment and inflammable materials like petrol, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the best extinguisher. The added advantage of CO2 is that in most cases it does not harm the electrical equipment.
It not only forms a blanket around the fuel fire and cut off oxygen supply, it also brings down the temperature of the fuel. That is why it is an excellent fire extinguisher.
Question 9. It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily.
Explain.
Answer : A heap of green leaves contains a lot of water and has very high ignition tempreture. Water is a natural fire extinguisher and do not let leaves catch fire easily where as dry leaves contains no water and have low ignition temprature and catch fire easily.
Question 10. Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer : A goldsmith use outermost zone of the flame with a metallic blow-pipe for melting gold and silver as it is the hottest part of flame.
Question 11. In an experiment 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer : Calorific value of the fuel = Amount of heat energy produced / Weight of Fuel burnt
= 180,000 /4.5 kJ/kg
= 40,000 kJ/J
Question 12. Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer :Yes, to some extent, the process of rusting can called slow combustion .The Rusting of iron is a oxidation process. In this iron using oxygen and water, gets oxidized and is rusted out.It is a slow process which does produce heat at a very slow rate. The combustion process is also a oxidation process and a chemical reaction by which fuel and an oxidizer react and produce heat or light. Combustion needs heat, an oxidizer, and fuel. Combustion is much faster than rusting.
Question 13. Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer : A candle flame is less hot near the wick as this is Innermost zone of unburnt wax vapours. where as outer most part of flame is the zone of complete combustion and is the hottest. There for, in case of Ramesh, water will get heated in a shorter time than that of Abida